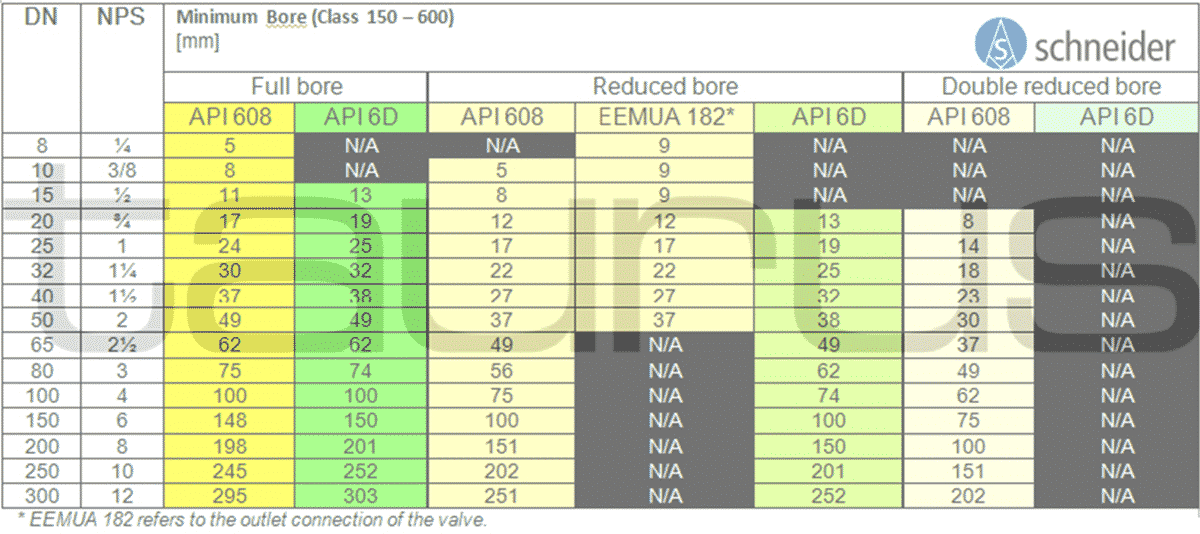
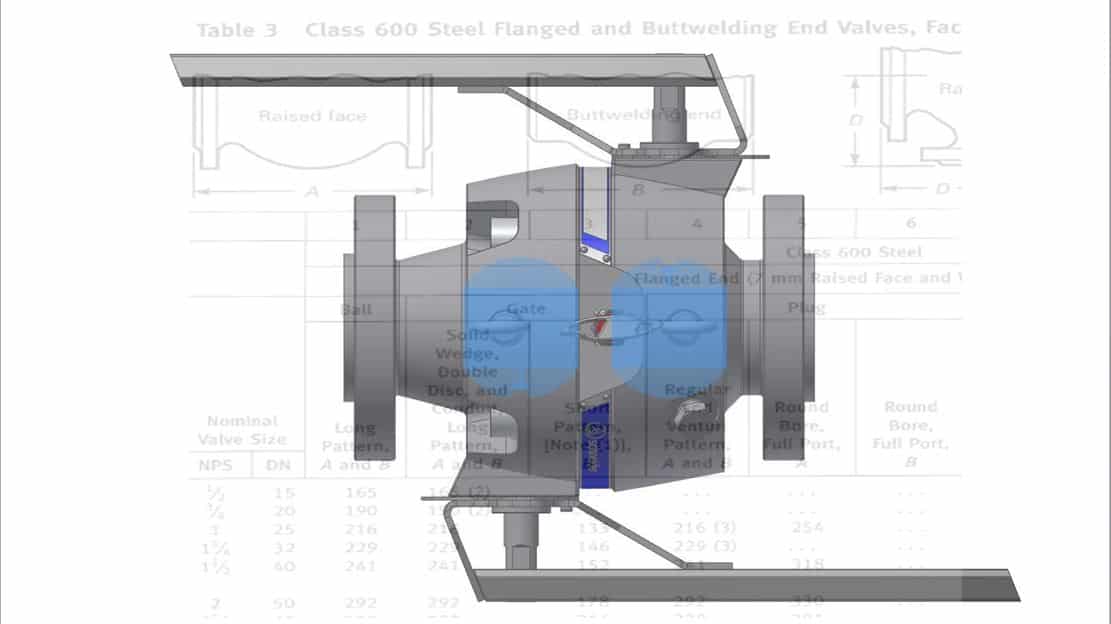
There has always been a lot of confusion and misunderstanding when it comes to Full Bore and Reduced Bore terminology. Let me try to explain some interesting facts. For example, DBB Valves are developed mainly for the use in the Oil and Gas sector. In this industry, the relevant design standards are ….
Continue readingFugitive Emissions: ISO 15848 vs. TA-Luft
Tracking and limiting Fugitive Emissions has moved into the focus of many countries around the world. Stringent legal requirements force the industry to rethink and use emission-reducing equipment. This sounds very simple, but from my experience there is still misconception when it comes to this subject.
Continue readingASME B16.10 – Exploring why it matters to DBB Valves
Ever since 1922, ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) has been defining pipeline safety upon demand from both industry and government. One of their standards has to do with face-to-face as well as end-to-end dimensions of straightway valves, centre-to-face and centre-to-end dimensions of angle valves. In this informative post, our primary focus will be on ASME B16.10 industrial valves.
Continue readingReplace a single ball valve by a Double Block & Bleed
When creating the design specification for our Taurus Series we came along the point ‘face to face’ dimensions. Immediately some colleague said “ASME B16.10 and EN 558 – but same length as a single ball valves for the Taurus DBB with 2 balls and a bleed in between?”
Well, we discussed that there might be a possibility to achieve this goal and we listed some values and benefits we could offer to our customers with such a short face to face dimension:
The major benefit would be that the new Double Block & Bleed (DBB) Pipeline Ball Valve (Taurus-Series) has the same face-to-face dimension as a single block ball valve. The length of a single block ball valve is specified in ASME B16.10 and APl 6D. As a consequence the valve can easily be installed into an existing pipeline without the need for any re-work on the pipeline.
Continue readingHow tight is your Valve Seat?
When people ask me, how tight our valve seats are, I usually get an increased heart rate and I most would like to say “Oh yes, they are very tight”.
But fun aside ….
Please note that I’m not talking about external tightness (stem sealing and body sealing), as there are already several accepted standards like ISO 15848-1, API 622, API 624, etc. which describe the evaluating of the valve design with respect to fugitive emissions. Those standards where driven by the legal environmental requirements and do not consider the internal tightness of the valve.
When talking about valves seat tightness, we have to differ between just a maximum leak rate of a production test and a seat performance test.
Continue reading“Fire Safe Approved” vs. “Fire Safe by Design”
During the last years I recognized, that people sometimes talk about “Fire Safe by Design“. When I was coming across this the first time, I wondered about the meaning of this in detail – Just using metal to metal sealing, graphite sealing or graphite packing?
“Fire safe by Design” is widely used, but to my knowledge there is no common or firm description or rules limiting or qualifying the use of this concept.
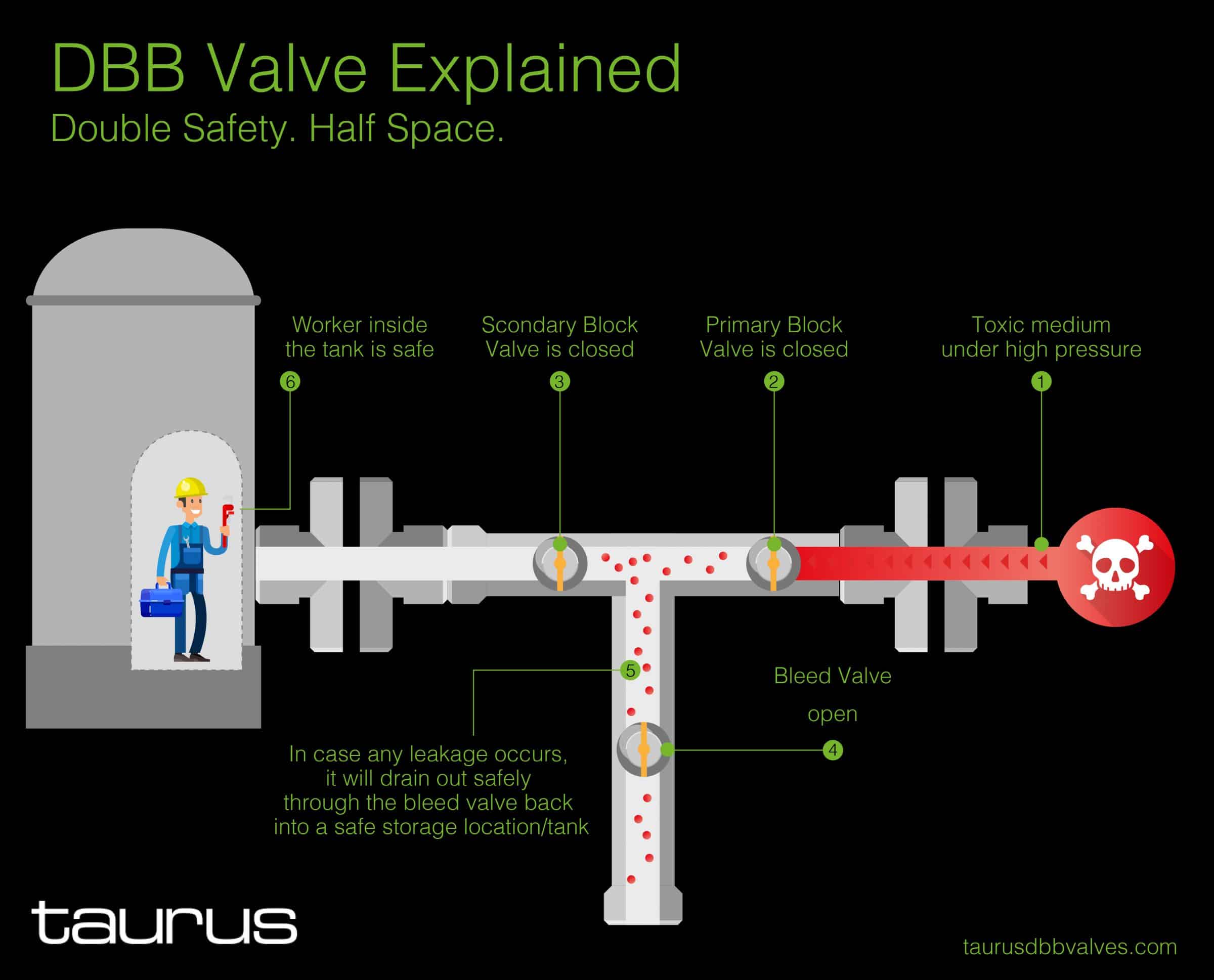
Continue readingDBB Valve Explained
I’m facing very often the situation where customers don’t understand the concept/purpose of the DBB functionality. Here is a simple infographic to explain one of the basic applications to protect the workers and the environment.
Continue readingFugitive Emissions: How to reduce it to protect the environment and improve plant safety
The European Union and United States and other countries are focusing on tracking fugitive emissions for certain industries. Today, fugitive emissions have become a major challenge to the environment as they are capable of harming the environment and even contribute to global warming.
Continue readingThe difference between Double Block & Bleed (DBB) and Double Isolate & Bleed (DIB)
Much confusion exists over the terminology and the differences between Double Block & Bleed Valves and Double Isolation & Bleed Valves. One point of confusion comes because many people using the term Double Block & Bleed really want a valve with Double Isolation & Bleed capabilities.
Continue reading